In the previous article, we looked at what influences the fiat interest rate in the fiat-money based economy.
The focus of this article is the crypto interest rate – what does drive it how much should it be?
We have three parts here:
1. We will look at the same factors, which are influencing interest in the fiat monetary system:
- The individual’s preferences to consume, invest or borrow
- The individuals preference short term versus long term borrowing or investment
- Rate of base-money production/destruction in the economy
- Rate of credit-money production/destruction in the economy
- The proximity of individuals to the “money creation” in society
2. We will calculate how much should be the crypto interest rate (interest without the credit risk) in the crypto economy.
3. In the end, we will compare the fiat monetary system with the crypto monetary system. It will show, which monetary system benefits which population segments.
1. Consumption preferences
Consummation preferences are presumably the same as in the fiat economy.
However, crypto users are rather younger generations / Millenials, which are characterized by relatively low saving rates and higher consummation preferences. i.e. the demand for borrowing is bigger than the demand for lending. This factor translates into higher interest.
2. Time preferences
Time preferences for crypto users are very similar to consummation preferences. This factor translates into higher interest as well.
3. Rate of base money creation /destruction
Rate of base-money production/destruction – Bitcoin, Ether, Dash, Litecoin, etc. have built-in growth mechanisms/inflation mechanisms, where miners are getting paid with the freshly minted crypto-coins for providing the infrastructure for the decentral networks.
These platforms are open source platforms, but the costs for running network infrastructure (hardware, bandwidth, and power) are real and they need to be financed. The built-in inflation mechanisms are the solution for financing the real network infrastructure costs.
This crypto-monetary expansion is at the moment following:
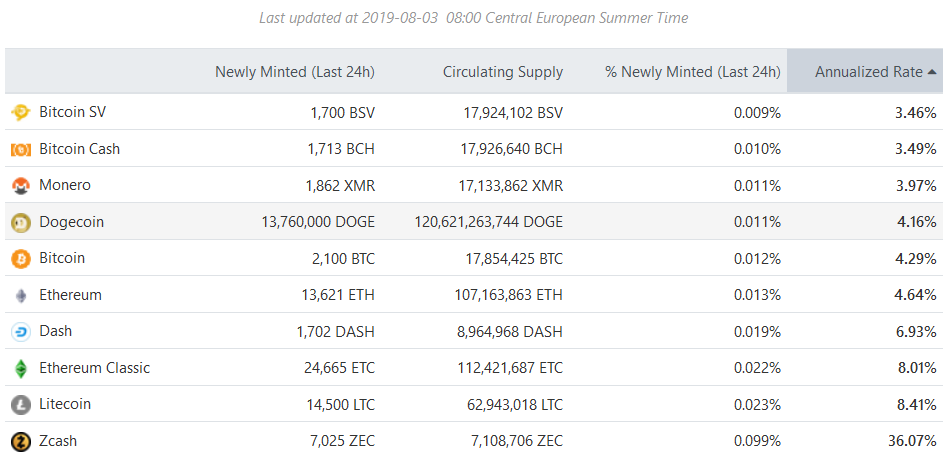
For example – Bitcoin monetary inflation is 4.29% per year and Litecoin monetary inflation is 8.41% per year.
4. Rate of credit money creation/destruction
Rate of credit money production/destruction – today’s fiat credit money – the commercial banking money, which is 90% of the total money – this is missing at the moment in the crypto economy. The crypto economy has only base-money. The crypto sector does not have credit-money yet.
The credit money has been around for the last 5’000 years, the first instances of the credit money are known from Mesopotamia and it was created in the peer to peer transactions. Credit money was created in peer to peer way for the first 4’700 years until the commercial banks started to emerge ca 350 years ago.
Then the “private credit money” of the commercial banks emerged and after the introduction of central banking, we arrived into our current “central credit money” incarnation.
Let’s put this in the perspective – our current fiat monetary system is 100 years old; the credit-money exists in different incarnations for the last 5’000 years. As credit-money has been around so long, we support the thesis, that it will emerge as well in the crypto sector.
5. Store of the value function
The store of value is very strong in Bitcoin. It’s called as well the “digital gold”. Store of the value function is present in other crypto-currencies as well, but less strong than in the Bitcoin.
Crypto-currencies are not manipulatable by the central instances as the base-money or credit-money in the fiat economy. This missing manipulation is the basis for the store of value in the crypto monetary system.
As there is no-manipulation compared with the fiat monetary system, then this results in higher demand for the crypto-currencies, which translates into higher interest.
6. Proximity to the money creation
Proximity to money creation – base-money is created by decentral means and it finances the miner’s operations. Decentral credit-money is still missing in the crypto sector, but it should be the only question of time until it will emerge.
If we decentral credit-money will emerge, then the proximity to money creation will equalize between the wealthy and the un-wealthy. It’s not only corporates and wealthy, who will be privileged, but everyone will be privileged to receive crypto credit or credit-money.
7. Summary of Factors
Here is the summary of the factors for the crypto-interest:
|
Factor |
Comment |
|
Consummation preferences |
Results in higher interest than the equilibrium |
|
Time preferences |
Results in higher interest than the equilibrium |
|
Rate of base money growth |
Bitcoin base-money is growing 4.29% per year; other main crypto-currencies are in the same area. It is less compared to the fiat world. |
|
Rate of credit money growth |
Credit money is yet missing in the crypto sphere. The total money growth ratio is therefore equal to the base money growth ratio. |
|
Proximity to money creation |
Market participants will have the same proximity to money creation. No-one has an advantage compared to the others |
|
Store of the value function |
High store of the value function, especially for the Bitcoin |
8. How much should be the interest in the crypto sector?
The following will answer the key question of this article – how much should be the base interest for the crypto sector – we look at this at the example of Bitcoin and Ethereum.
|
Factor |
Bitcoin |
Ethereum |
|
Consumption preferences |
Younger population results in higher interest |
Younger population results in higher interest |
|
Time preferences |
Younger population results in higher interest |
Younger population results in higher interest |
|
Rate of base-money growth |
4.29% per year |
4.64% per year |
|
Rate of credit-money growth |
0.00% – it’s missing at the moment |
0.00% – it’s missing at the moment |
|
Store of the value function |
High store of the value function drives the interest higher |
Medium store of value function has a positive impact on the interest |
|
Base interest per year |
7% – 8% |
6% – 7% |
These would be the estimated base rates for the crypto base interest rates. i.e.if lending crypto, then the interest rate should start from this area.
9. Comparison of fiat interest rate versus crypto interest rate
This table summarizes the above discussion:
|
Interest rate parameter |
Fiat monetary system |
Crypto monetary system |
|
Consumption preferences |
Less impact than in the crypto sphere |
Rather younger populous implies higher consummation preferences, resulting in higher interest |
|
Time preferences |
Less impact than in the crypto sphere |
Rather younger populous implies shorter time preferences, resulting in higher interest |
|
Rate of base money growth |
300% to 1’000% depending on the central bank in the last 12 years |
4% – 8% per year depending on the crypto |
|
Rate of credit money growth |
6% of total money growth per year |
0.00% |
|
Proximity to the money creation |
The ones with high proximity to the money creation have preferred terms |
No preferred segments |
|
Store of the value function |
Low store of the value due to continuous monetary inflation |
High store of the value |
10. Which monetary system prefers whom?
Fiat money is inflationary money, with a low store of the value function. It’s the money, which benefits the ones, with high proximity to the money creation, but not the general population. It benefits the few and not the many.
The benefitted ones have better credit conditions and are paying less interest than the required base-interest in the economy. This results in the continuous wealth transfer between the benefitted ones (at the cost of all other segments).
Crypto money is at the first-hand high store of value money. There are no preferred segments, the proximity to the money creation is the same for all. This money benefits the general population. It benefits the many and not the few.
Summary
This article analyzed which parameters influence the crypto interest rate and how much the crypto interest rate should be.