🕌 BREAKING: The $3 trillion Islamic finance market finally has its first true DeFi solution. For 1.8 billion Muslims worldwide, earning passive income from cryptocurrency has been impossible due to religious restrictions… until now. Discover how BarakaFi makes halal DeFi accessible for the first time in history.
рџЊ™ Start Your Halal DeFi Journey Today
100% Sharia-compliant • Riba-free • Certified by Islamic scholars
First, about SmartCredit.io
SmartCredit.io has been at the forefront of DeFi for 5 years, pioneering P2P (peer-to-peer) DeFi solutions as opposed to the industry-standard P2P2P (Peer-to-Pool-to-Peer) model that dominates the crypto lending space.
The main reason for this architectural choice is profound: P2P2P is a much more regulated activity than P2P because it involves pooling assets—a heavily regulated financial activity that usually requires a banking license in most jurisdictions.
P2P systems like SmartCredit.io represent a much less regulated approach because they function as a pure marketplace where borrowers and lenders meet directly through crypto lending platforms, without intermediary asset pools.
However, there is one transformative advantage of P2P that goes beyond regulatory simplicity—P2P systems are the only architecture that can enable halal banking and Islamic finance in the blockchain space, which other Web3 companies following the P2P2P paradigm cannot provide.
This revelation has profound implications: traditional DeFi cannot serve Islamic Finance. This means Web3 Finance must evolve into two distinct but complementary clusters:
- Web3 Decentralized Finance – utilizing the P2P2P paradigm (traditional DeFi)
- Web3 Islamic Finance – utilizing the P2P paradigm (halal DeFi)
This article analyzes both clusters and explains how Sharia-compliant blockchain solutions can revolutionize decentralized finance for 1.8 billion Muslims worldwide seeking halal cryptocurrency investment options.
рџ’Ў Did You Know? The global Islamic finance market is valued at over $3 trillion, yet less than 0.1% of this market has access to blockchain-based solutions. BarakaFi is changing that.
What is DeFi?
DeFi (Decentralized Finance) represents a fundamental shift in how people control their financial assets. In DeFi, users maintain complete control over their assets through their personal wallets, without relying on centralized intermediaries.
The critical difference between centralized finance and DeFi is that DeFi is self-custodial—DeFi providers cannot access users’ private keys, and only wallet owners (private key holders) can authorize and execute transactions. This creates unprecedented financial sovereignty.
DeFi emerged with two primary innovations:
- Decentralized Borrow/Lend Systems
- Decentralized Exchange Systems (DEXs)
How Traditional DeFi Lending Works (P2P2P Model)
Decentralized Borrow/Lend protocols use “Money Market” concepts, where lenders pool their assets together into a common liquidity pool. An automated algorithm (often an oversimplified utility function) sets interest rates dynamically based on supply and demand. The generated interest is then distributed between the lenders who provided liquidity and the platform itself.
Because of this asset pooling architecture, these are fundamentally P2P2P systems—every user interacts with a shared pool rather than with specific individuals. Borrowers borrow from the pool, and lenders add funds to the pool.
How Decentralized Exchanges Work (Also P2P2P)
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs) utilize Automated Market Maker (AMM) systems. Unlike traditional order book exchanges, AMMs are pooling-based systems. Prices are algorithmically determined using mathematical functions (typically hyperbolic curves)—there will always be a price based on the pool’s position on its respective curve.
DEXs also rely on asset pooling. They aggregate assets from liquidity providers, who receive a portion of trading fees as compensation. This means assets are pooled, and providers receive interest-like payments on their contributed assets.
The Islamic Finance Problem with Traditional DeFi
In both DeFi lending and DEX cases, we encounter two fundamental characteristics that conflict with Islamic finance principles:
- Asset pooling – Multiple users’ funds are mixed together
- Asset providers receive fixed returns (interest) on their pooled assets
From a regulatory perspective, this structure creates securities products that must be registered in jurisdictions where they’re marketed—a complex compliance burden.
More critically, these products cannot be used for Islamic Finance because of their asset pooling and interest-based payment structures, which violate Sharia law principles.
рџљЂ Be Among the First 10,000 Users
Join the halal DeFi revolution and earn riba-free returns
What is Islamic Finance?
Islamic Finance represents a comprehensive ethical banking system based on Sharia law that sets specific principles and limitations compared to conventional “Western” banking models. These halal finance principles ensure that all financial activities are riba-free (interest-free) and fully compliant with Islamic law.
The fundamental principles of Islamic Finance include:
Core Sharia Finance Principles:
- Pure P2P Structure Required – Asset pooling is strictly prohibited; every transaction must be directly between two identifiable parties
- Risk Must Be Shared – The lender must bear genuine risk; there can be no guaranteed return without sharing potential losses
- Riba (Interest) is Forbidden – Fixed interest payments are prohibited; earnings must come from legitimate profit-sharing or service fees
- Asset-Backed Transactions – All financing must be backed by real, tangible assets
- Ethical Investment – Funds cannot support prohibited activities (alcohol, gambling, pork, weapons, etc.)
While many in the Western world may be unfamiliar with these principles, there exists a thriving parallel ecosystem of Islamic banking that serves more than 1.8 billion Muslims worldwide who actively seek halal investment options and Sharia-compliant financial services.
The $3 Trillion Opportunity
The global Islamic finance industry is valued at over $3 trillion and growing at 10-12% annually. Yet despite this massive market, there have been virtually no Web3 solutions serving this ecosystem—until now.
This means the vast majority of the Muslim population cannot use conventional DeFi borrowing/lending solutions due to non-compliance with Sharia law. They’ve been excluded from the cryptocurrency revolution despite having both the interest and the capital to participate.
The implication is profound: Web3’s reach and global impact could increase dramatically if Sharia-compliant DeFi and halal blockchain solutions were made accessible. However, Web3 DeFi in its current form fundamentally cannot serve Islamic Finance without architectural changes.
⚠️ The Current Problem: 1.8 billion Muslims (23% of the world’s population) are effectively locked out of DeFi due to religious restrictions. BarakaFi solves this by building the first truly Sharia-compliant DeFi platform.
Why Traditional DeFi Cannot Serve Islamic Finance Today
Let’s examine the specific incompatibilities between traditional DeFi architecture and Islamic finance requirements:
1. Architecture Mismatch: P2P2P vs P2P
Islamic Finance requires pure P2P (peer-to-peer) systems. However, today’s DeFi lending and borrowing platforms are built exclusively on P2P2P (peer-to-pool-to-peer) systems. This architectural difference isn’t just technical—it’s fundamentally incompatible with Sharia law.
In P2P2P systems, your funds mix with everyone else’s in a pool. You don’t know who borrows your money, and borrowers don’t know whose money they’re using. This anonymity and pooling violates Islamic finance principles.
2. Identity and Transparency Requirements
Islamic Finance requires the source of funds to be known. When assets are pooled on the lender’s side, no single individual lender can be identified by the borrower—a critical violation of halal finance requirements.
Sharia law mandates transparency in financial relationships. Both parties must know exactly whom they’re transacting with, creating accountability and ethical responsibility.
3. The Riba (Interest) Problem
We established earlier that riba (interest) is absolutely prohibited in Islamic banking. Traditional DeFi platforms generate returns through interest-bearing mechanisms, making them inherently non-compliant.
The Quran explicitly forbids riba in multiple verses, and this prohibition is non-negotiable for practicing Muslims.
4. Risk-Sharing Requirement
In Islamic finance, both the lender and borrower must share genuine risk. Traditional DeFi often protects lenders through over-collateralization while placing all risk on borrowers—another Sharia violation.
The Islamic principle is clear: profit must be accompanied by the possibility of loss. Guaranteed returns without risk exposure are considered exploitative and prohibited.
Summary: Why Current DeFi Fails Islamic Finance
Here are the key incompatibilities preventing traditional DeFi from serving Islamic finance:
- вќЊ P2P2P architecture instead of required pure P2P systems
- вќЊ Interest-based returns (riba) are used instead of profit-sharing or service fees
- вќЊ No genuine risk-sharing between lenders and borrowers
- вќЊ Anonymous asset pooling obscures transaction parties
- вќЊ No Sharia certification or Islamic scholarly oversight
These fundamental incompatibilities mean that none of the existing major DeFi platforms (Aave, Compound, MakerDAO, etc.) can be used for Islamic banking without complete architectural redesign to support Sharia-compliant cryptocurrency lending.
| Feature | Traditional DeFi | Islamic DeFi (BarakaFi) | Sharia Compliant? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Asset Pooling | вњ… Yes (P2P2P) | вќЊ No (Pure P2P) | вњ… |
| Interest (Riba) | вњ… Interest-based | вќЊ Riba-free | вњ… |
| Risk Sharing | вќЊ Lender protected | вњ… Both share risk | вњ… |
| Transaction Transparency | вќЊ Anonymous pooling | вњ… Direct P2P visibility | вњ… |
| Sharia Certification | вќЊ Not certified | вњ… Scholar-approved | вњ… |
| Halal for Muslims | вќЊ NO | вњ… YES | вњ… |
вњ… BarakaFi: 100% Sharia-Compliant DeFi
Experience the first truly halal DeFi platform built for Muslims
What is Required for Islamic Finance in DeFi?
Building a truly Sharia-compliant DeFi platform requires fundamental architectural changes and innovative mechanisms. Let’s examine the specific requirements for halal DeFi:
1. Riba-Free Service Fee Structure
The Challenge: Interest (riba) is absolutely prohibited in Islamic Finance.
The Solution: Service fees can be charged to borrowers instead of interest, creating a riba-free lending structure. These fees compensate the platform for its services rather than representing interest on loaned capital.
This distinction may seem subtle, but it’s theologically significant: service fees are permissible because they represent payment for actual work performed, whereas interest represents earning money simply from having money—a key difference in Islamic economic philosophy.
2. Sell-and-Buy-Back Transaction Structure
The Challenge: Traditional loans with interest repayment violate Sharia law.
The Solution: Loan transactions are structured as sell-and-buy-back contracts (Murabaha in Islamic finance). Here’s how it works:
- Borrowers sell their collateral assets at a discount to lenders (this represents the “loan”)
- A predetermined buy-back price is established at the contract’s initiation
- Later, borrowers can buy back their assets at the pre-agreed price (representing “loan repayment”)
- If the borrower chooses not to buy back, the lender retains ownership of the asset purchased at discount
This structure transforms what appears to be a loan into a legitimate asset purchase and resale transaction, making it Sharia-compliant while achieving the same economic function as traditional lending.
3. Collateral Protection with Sharia Compliance
The Challenge: Protecting lenders while maintaining Islamic principles during market volatility.
The Solution: Special mechanisms protect lenders while staying halal. When lenders purchase borrowers’ assets at a discount, borrowers can later repurchase at a predetermined discount rate. But what happens when the asset’s market price falls below the predetermined discount rate?
In this scenario, similar to how collateral ratios work in traditional DeFi, the contract is terminated and asset ownership transfers to the lender. This protects the lender from catastrophic loss while maintaining the integrity of the original sale contract—keeping the transaction halal.
4. Risk-Sharing Mechanisms with Loss Provision Fund
The Challenge: Islamic banking mandates that lenders must share risk—there should be no guaranteed return without genuine risk exposure.
The Solution: A Loss Provision Fund can be established to distribute risk fairly across the system. A small percentage of each borrower’s service fee is allocated to this collective fund, which covers unexpected losses from defaults or market crashes.
This mechanism ensures:
- Lenders bear genuine risk (fund might be depleted in severe downturns)
- Risk is shared across all participants (Islamic principle of mutual cooperation)
- System remains stable even during market volatility
- No individual lender faces catastrophic loss
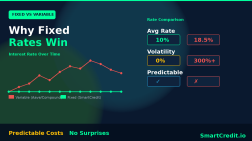
5. Transparent Discount Rate Structure (Replacing Interest Rates)
The Challenge: How to price the cost of financing without using interest rates?
The Solution: The concept of interest rates transforms into discount rate differentials. Here’s the mechanism:
- The borrower sells their asset at discount rate R1 (lower price)
- The borrower later repurchases at discount rate R2 (higher price)
- The difference between R1 and R2 represents the cost of financing
- This is economically similar to interest but structured as a legitimate price differential on asset transactions
This pricing structure achieves market efficiency while remaining fully Sharia-compliant because it’s based on real asset transfers rather than interest accumulation.
6. Direct Peer-to-Peer Transparency (Pure P2P)
The Challenge: Maintaining complete transparency about transaction counterparties.
The Solution: Implementing true P2P architecture where:
- Borrowers know exactly from whom funds originate
- Lenders know exactly to whom their funds are going
- Asset pooling is completely eliminated
- Every transaction is directly between two identified parties
- Full audit trail maintains accountability
This level of transparency is technically challenging to implement efficiently but is non-negotiable for Sharia compliance.
Complete System Requirements Summary
A truly halal DeFi platform must implement:
- вњ… Pure P2P architecture (no asset pooling)
- вњ… Automated or manual discount rate setting system (not interest rates)
- вњ… Service fee system (instead of interest payments)
- вњ… Loss Provision Fund for risk distribution
- вњ… Liquidation system for terminating contracts when necessary
- вњ… Full transparency of transaction counterparties
- вњ… Sharia scholar certification and ongoing oversight
This is exactly what BarakaFi has built—the world’s first platform meeting all these requirements.
💬 “As a Muslim investor, I’ve been waiting for a halal DeFi solution for years. BarakaFi finally makes it possible to earn passive income without compromising my faith. I’m earning 10%+ APY completely riba-free while knowing exactly who I’m transacting with. This is revolutionary.” – Ahmed K., Early BarakaFi User
What’s Required for the Success of Web3 Finance?
Our analysis reveals a critical insight: traditional DeFi fundamentally cannot meet Islamic Finance requirements without complete architectural redesign.
Simultaneously, there exists a vast, dramatically underserved market: 1.8 billion Muslims seeking halal finance and Sharia-compliant cryptocurrency investments, representing $3+ trillion in potential capital.
The Two-Cluster Solution
We propose splitting Web3 Finance into two complementary but distinct clusters:
- Traditional DeFi – with AMMs and Money Markets that pool assets (serving non-Muslims and Muslims who accept interest-based systems)
- Islamic Finance – strictly P2P systems where assets are never pooled (serving the 1.8 billion Muslims requiring halal options)
This means evolving from the current limited model:
Current Reality: Web3 Finance = DeFi only
This excludes 1.8 billion Muslims from the crypto revolution
To an inclusive, comprehensive model:
Future Vision: Web3 Finance = DeFi + Islamic Finance
This serves ALL global populations with appropriate financial solutions
The Market Opportunity is Massive
Today’s reality is that “Web3 Finance = DeFi” actively excludes highly motivated Web3 enthusiasts in Islamic countries who desperately want halal DeFi solutions but have no viable options.
Consider the numbers:
- рџ“Љ 1.8 billion Muslims currently locked out of DeFi
- рџ’° $3+ trillion Islamic finance market with no blockchain access
- рџ“€ 10-12% annual growth in Islamic finance globally
- рџЊЌ 50+ Muslim-majority countries with minimal DeFi adoption
- рџљЂ 400+ million unbanked Muslims who could access DeFi directly
In the future, we must add “Islamic Finance” to the Web3 equation, which would trigger explosive growth in Web3 Finance and provide riba-free blockchain alternatives to hundreds of millions of currently excluded users!
Why This Benefits Everyone
Creating Islamic Finance infrastructure in Web3 doesn’t just serve Muslims—it benefits the entire ecosystem:
- рџЊђ Massively expands the addressable market for crypto adoption
- рџ’Є Increases network effects through greater participation
- рџ›ЎпёЏ Creates more ethical financial systems through transparency requirements
- рџ¤ќ Bridges cultural divides between Western and Islamic finance
- рџ“љ Innovates new DeFi architectures that could benefit all users
The Islamic finance principles of transparency, risk-sharing, and ethical investment can make DeFi better for everyone—not just Muslims.
Ready to Experience Halal DeFi?
Join BarakaFi and access the first truly Sharia-compliant DeFi platform built on SmartCredit’s proven P2P technology.
100% Sharia-compliant • Riba-free • Scholar-certified • Join 10,000+ users
Get Started with Sharia-Compliant DeFi
SmartCredit.io, in partnership with Haqq Network, has pioneered BarakaFi.com—the world’s first truly halal DeFi platform. Our revolutionary P2P lending solution ensures complete Sharia compliance while delivering competitive returns:
вњ… Why BarakaFi is Different
| Feature | Traditional Islamic Banks | Traditional DeFi | BarakaFi |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sharia-Compliant | вњ… Yes | вќЊ No | вњ… Yes |
| Returns (APY) | 0.5-2% | 5-15% | 8-12% |
| 24/7 Access | вќЊ No | вњ… Yes | вњ… Yes |
| Global Access | вќЊ Limited | вњ… Yes | вњ… Yes |
| Transparency | вљ пёЏ Medium | вљ пёЏ Pooled | вњ… Full P2P |
| Minimum Amount | $10,000+ | $10+ | $10+ |
рџЊ™ BarakaFi Core Features
- ✅ 100% Sharia-compliant lending – Certified by Islamic scholars from Haqq Network
- ✅ Riba-free transactions – Service fee model instead of interest
- ✅ Transparent P2P structure – Know exactly who you’re transacting with
- ✅ Risk-sharing mechanisms – Loss Provision Fund protects all participants
- ✅ Competitive returns (8-12% APY) – 10-50x better than traditional Islamic banks
- ✅ Global accessibility – Serve Muslims worldwide, 24/7
- ✅ Low minimums – Start with as little as $10
- ✅ Built on proven technology – SmartCredit’s 5 years of DeFi experience
Ready to explore halal cryptocurrency investment? Learn more about using crypto as collateral in a Sharia-compliant way.
Frequently Asked Questions About Islamic DeFi
Is Bitcoin halal?
Bitcoin and cryptocurrency in general are subjects of ongoing scholarly debate in Islamic jurisprudence. While some scholars have concerns, many prominent Islamic scholars have ruled that cryptocurrencies are permissible (halal) as long as they’re not used for prohibited activities.
What matters most for BarakaFi users: Regardless of debates about specific cryptocurrencies, BarakaFi ensures all transactions are Sharia-compliant. We structure lending as asset purchase and resale contracts, eliminate riba, maintain P2P transparency, and ensure risk-sharing—making the platform halal regardless of which digital assets are used as collateral.
How do I know BarakaFi is truly Sharia-compliant?
BarakaFi has undergone rigorous review and received certification from Islamic scholars associated with Haqq Network, a blockchain platform specifically designed for Sharia compliance in digital finance.
Our compliance is ensured through:
- Pure P2P architecture (no asset pooling)
- Riba-free service fee model (no interest)
- Risk-sharing through Loss Provision Fund
- Sell-and-buy-back transaction structures
- Complete transparency of counterparties
- Ongoing oversight by Islamic finance experts
Can I really earn passive income without riba?
Absolutely! The key difference is how you earn. Instead of interest (riba), you earn through:
- Profit-sharing – You share in the legitimate economic gains from financing real economic activity
- Service fees – You’re compensated for providing a valuable financial service
- Asset appreciation – Your returns come from actual economic value creation, not mere time-value of money
This distinction might seem subtle, but it’s theologically crucial: you’re earning from genuine economic participation and risk-sharing, not from charging interest on loaned money. Many BarakaFi users earn 8-12% APY completely riba-free.
What if I’m not Muslim—can I still use BarakaFi?
Absolutely! Islamic finance principles like fairness, transparency, ethical investment, and risk-sharing benefit everyone regardless of religious background.
Many non-Muslims choose Islamic finance because they appreciate:
- Ethical investing that excludes harmful industries
- Greater transparency and accountability
- More equitable risk distribution
- Asset-backed financing (less speculative)
BarakaFi welcomes users of all faiths and backgrounds who want to participate in more ethical DeFi.
How does BarakaFi compare to traditional Islamic banks?
BarakaFi offers numerous advantages over conventional Islamic banks:
| Advantage | Details |
|---|---|
| 10-50x Better Returns | Earn 8-12% APY vs 0.5-2% at traditional Islamic banks |
| 24/7 Access | Transact anytime, anywhere—no banking hours |
| Near-Zero Fees | DeFi efficiency eliminates most overhead costs |
| Global Accessibility | Serve Muslims anywhere, not just in Muslim-majority countries |
| Complete Transparency | Blockchain provides full audit trail and P2P visibility |
| Low Minimums | Start with $10, not $10,000+ |
How does the Loss Provision Fund work?
The Loss Provision Fund is a crucial innovation that enables risk-sharing while protecting the system:
- A small percentage of each borrower’s service fee goes into the collective fund
- If a borrower defaults or liquidation occurs with losses, the fund covers it
- This distributes risk across all participants (Islamic mutual cooperation principle)
- Lenders earn returns but also bear genuine risk (fund could be depleted)
- The system remains stable even during market downturns
This mechanism satisfies the Sharia requirement that “there should be no return without risk” while making the platform practical and sustainable.
What cryptocurrencies can I use with BarakaFi?
BarakaFi supports major cryptocurrencies as collateral, including ETH (Ethereum), BTC (Bitcoin), and stablecoins. The platform focuses on ensuring that all transactions are Sharia-compliant regardless of which digital assets are used.
Visit BarakaFi.com for the current list of supported assets and learn more about crypto lending platforms.
Is my money safe on BarakaFi?
BarakaFi is built on SmartCredit’s proven infrastructure with 5 years of security track record:
- рџ”’ Smart contracts audited by leading security firms
- 🛡️ Self-custodial wallets—you control your private keys
- рџ“Љ Transparent blockchain records for all transactions
- вљ–пёЏ Collateral protection mechanisms prevent losses
- рџ’° Loss Provision Fund provides additional security layer
As with all DeFi platforms, users should understand the risks and never invest more than they can afford to lose.
How to Get Started with BarakaFi
Step 1: Connect Your Wallet
Visit BarakaFi.com and connect your cryptocurrency wallet (MetaMask, WalletConnect, or other supported wallets). This takes less than 30 seconds.
Step 2: Choose Your Role
Decide whether you want to:
- Lend (Earn passive income) – Earn 8-12% APY on your cryptocurrency by lending to verified borrowers
- Borrow (Access liquidity) – Use your crypto as collateral to borrow funds without selling your assets
Step 3: Complete Your First Transaction
Follow the simple on-screen instructions to complete your first halal DeFi transaction. The platform guides you through each step to ensure Sharia compliance.
Step 4: Monitor and Manage
Track your positions, earnings, and transactions through the intuitive BarakaFi dashboard. Enjoy complete transparency into your Islamic finance activities.
вљЎ Early Adopter Opportunity: BarakaFi is currently in its growth phase. Early users benefit from higher returns as the platform establishes its initial liquidity pools. Join now to maximize your halal earnings!
The Future of Islamic Finance in Web3
BarakaFi represents just the beginning of Islamic Finance integration into Web3. The roadmap includes:
- 🌍 Global Expansion – Serving Muslims in 50+ countries with localized support
- 📱 Mobile Applications – iOS and Android apps for on-the-go halal DeFi access
- 🤝 Partnership Ecosystem – Integration with Islamic banks and financial institutions
- 📚 Educational Resources – Comprehensive guides on Islamic finance in the blockchain era
- 🎓 Scholar Network – Expanding Sharia advisory board for ongoing compliance
- 💼 Institutional Products – Solutions for Islamic investment funds and wealth managers
- 🔄 More Financial Products – Halal trading, savings, and investment tools
By participating in BarakaFi today, you’re not just accessing halal DeFi—you’re helping build the future of Islamic finance for 1.8 billion Muslims worldwide.
Additional Information
- SmartCredit.io – P2P DeFi Lending Platform (5 years proven track record)
- BarakaFi.com – World’s First Halal DeFi Platform (Start earning today!)
- Crypto as Collateral Guide – Learn how to use cryptocurrency for halal lending
- Crypto Lending Platforms – Compare different DeFi lending options
- SmartCredit Education Hub – Complete DeFi tutorials and guides
Follow us on Social Media
- Twitter: https://twitter.com/smartcredit_io
- Gitbook: https://learn.smartcredit.io
- Telegram: https://t.me/SmartCredit_Community
- Haqq Network: https://haqq.network/
- BarakaFi Announcement: BarakaFi Launch Article