In the middle of February, the bZx (https://bzx.network ) got вҖңhackedвҖқ. However, this was not via the technical means but the usage of bZx and the related platforms. Therefore letвҖҷs call it a вҖңusage hackвҖқ because this hack was executed via fully legal means of using the DeFi ecosystem.
Several analyses were published. For example, click here or here.
Fast comments were published in the response that the hack was feasible only because of the source code errors in bZx smart contracts and that after fast fixing the source code errors everything is back to the business as normal.
Is it so?
At SmartCredit.io we do not think so вҖ“ our view is that the вҖңusage hacksвҖқ in the DeFi are still feasible because of how collateral price discovery on the exchanges is implemented and how the collateral value calculations are executed. ItвҖҷs because of how the credit-risk management has been implemented in the DeFi systems (or rather very little implemented).
Collateral price discovery on the exchanges
The key element of the bZx hack was the manipulation of the collateral price, which allowed the attacker to take a loan against an overpriced collateral asset. This allowed the hacker to achieve high leverage via the manipulated collateral price, which then resulted in a high profit for the attacker.
But how are the collateral assets priced? LetвҖҷs see how the price is set on the exchanges. We have two ways for the price discovery on the exchanges:
- Via the bid / ask order books вҖ“ thatвҖҷs how all central exchanges are doing this
- Via the вҖңsmart formulaвҖқ, which would calculate the price, even if the bids/asks are missing
LetвҖҷs look on the 0x вҖ“ they represent the Type 1 exchange. The price is determined by the existing bids and asks in the order book. However, if the order book is not filled, then it will be easy to manipulate the price of the asset.
LetвҖҷs look at the Uniswap Exchange вҖ“ it represents the Type 2 exchange. The price on the exchange is set automatically via the following formula A x B = C (A and B are prices of an asset pair, and C is a constant). If we add a lot of A or B into the respective contract, then we will manipulate the price of the asset in the very short term and very much. ThatвҖҷs how the price of the collateral assets was manipulated in the bZx usage hack.
Both types of exchanges can be manipulated via usage. So, the operating assumption for collateral-based lending should be manipulated at any time. Therefore the safeguards for calculating the collateral value are required.
How to execute usage hacks?
bZx has fixed the source code errors, which simplified the hack. But the usage hacks on the DeFi platforms are still possible:
The following steps are required:
- Identify collateral, which is accepted in the decentral lending
- Identify how the respective lending system is receiving collateral price data вҖ“ from one exchange or multiple exchanges
- Manipulate the prices of the collateral up at the respective exchanges (Uniswap, 0x, Kyber Protocol)
- Take a loan on the decentral lending platform against a manipulated collateral
- Sell the manipulated collateral on the top
- Let the loan to default (the attacker has received an asset already, he does not plan to pay it back and he will lose his collateral. This collateral serves as a security for the loan, it is however not enough to cover the loan face value after the collateral price has bounced back to the equilibrium price)
Collateral ratios
Here are the current collateral ratios of DeFi lending protocols (Source: https://loanscan.io/supplied-liquidity ). We see on average 400% collateral for the loans, which means the prices have to be manipulated at least by factor 4 for having a profit from the above scenario. In case you ask, why are the DeFi collateral ratioвҖҷs so high вҖ“ see the answer in our analysis.
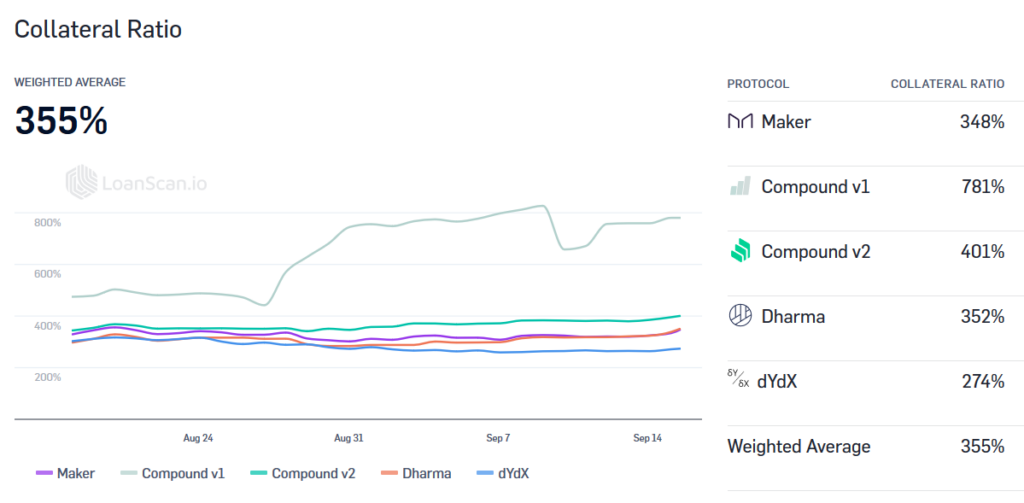
Why was the hack done on the bZx? ItвҖҷs because the bZx used lower collateral ratios than the current 400+ %. Additionally, they used only one price feed for the collateral value calculation, which required to manipulate the price only on one exchange.
How to mitigate usage hacks?
There are multiple ways to mitigate вҖңusage hacksвҖқ. However, proper mitigation will require proper credit risk management procedures.
The first mitigation would be to use the price oracles, which use the aggregate prices from different exchanges for the collateral asset вҖ“ it is more difficult to manipulate many exchanges simultaneously than just one or two exchanges. Additionally, we would need not only decentral exchange prices feeds, but central exchange price feeds as well.
But this is not enough вҖ“ the spot prices on multiple exchanges can be manipulated in parallel.
The second mitigation is to use the moving averages for the collateral calculation instead of the spot prices. The moving average should be calculated based on the aggregate price from the multiple exchanges. LetвҖҷs assume we will use the 30-day moving average. LetвҖҷs assume that the spot-prices on the multiple exchanges will be manipulated simultaneously вҖ“ we would be protected by using the moving average because it takes much more than just the spot price (or flash crash) to move the moving average up or down.
The third mitigation would be to use the moving averages over the aggregate prices from multiple exchanges with the standard deviations. Standard deviations can be calculated for any price series. The price series with high volatility would have a high standard deviation and vice versa. Having smaller standard deviations would indicate a smaller probability of price manipulations and vice versa.
How do we address usage hacks in SmartCredit.io?
In SmartCredit.io we are prepared for the usage hacks. The high-level procedure looks as follows:
- We look at the spot price, moving average, and standard deviation of the collateral
- If these parameters match, then we use the spot price for collateral calculation
- If these parameters do not match (either because of the price manipulation or the flash crashes), then we use the moving averages price for the collateral calculation
SmartCredit.io is a hybrid DeFi solution. The borrowing and lending happen on the blockchain. In parallel, we do have off-chain components, which are doing calculation intense tasks.
SmartCredit.io is not driven by a fundamental wish to put everything on the blockchain, but by a pragmatic drive to provide pragmatic solutions to a real business needs вҖ“ to the implementation of the credit-markets on the blockchain.
These are the reasons for hybrid DeFi solutions:
- Scalability
- Usability
- Credit risk management
For more information about the SmartCredit.io re-inforcing ecosystem have a look at this article. For more information about the crypto lending market, see our other analysis.
What is the way forward after the bZx hack?
The DeFi protocols are open source, the lending and borrowing via the smart contracts are pretty straight forward. However, credit risk management is where the rubber hits the road. This will differentiate the crypto lending systems from each other.
As this will be very business-critical know-how, then we doubt, that credit risk management will be ever open source. Additionally, credit risk management will be calculation intense. This leads us to the hybrid solutions consisting of the blockchain-based lending contracts and off-chain calculation intense components.
The market will be fragmented in the following way:
- There will be crypto lending systems with limited credit risk management (current DeFi solutions). These systems will use high collateral requirements and treat every loan as the potential candidate for a default. The borrowers have to pay very high collateral on these systems because over-collateralization is all the credit risk management these platforms have
- Other systems will implement credit risk management. They will be hybrid solutions. These systems will offer additional benefits to the users вҖ“ for example like SmartCredit.io offering 2x smaller collateral requirements than the standard DeFi products
If you liked this article, then please share it!